Production of Monoclonal vs. Polyclonal Antibodies
Homogeneous antibody populations (monoclonal antibodies) can be elevated by fusion B lymphocytes with eternal cell culture to produce hybridism. Hybridism will produce many copies of the exact same antibodies. If you want the best antibody services then you can navigate to this site.
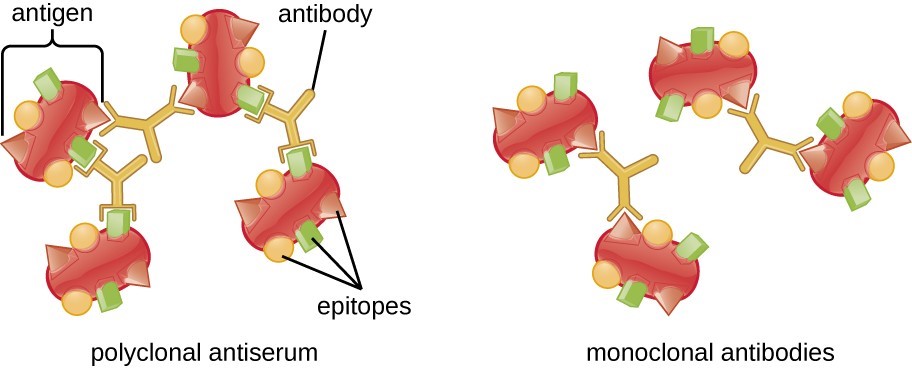
Image Source: Google
This impressive phenomenon has played a role in developing antibodies for diagnostic applications since monoclonal antibodies respond with one epitope in antigens.
However, they are more susceptible to the loss of epitope through antigen chemical treatment rather than polyclonal antibodies. This can be balanced by combining two or more monoclonal antibodies to the same antigen.
Some beneficial properties of polyclonal antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies often identify several epitopes, making it more accepting of minor changes in the environment of antigens. Polyclonal antibodies can be produced in various species, including rabbits, goats, sheep, donkeys, and others, which gives users a lot of options in experimental design.
Polyclonal antibodies target several epitopes and so they generally provide stronger detection.
Some beneficial properties of monoclonal antibodies
Because of their specificity, monoclonal antibodies are very good as the main antibodies in the test, or to discover antigens in the network, and will often produce fewer background signals than polyclonal antibodies.
When compared to polyclonal antibodies, the homogeneity of monoclonal antibodies is very high.
If experimental conditions remain constant, the results of monoclonal antibodies will be very reproduced among experiments.
The specificity of monoclonal antibodies creates it very efficient to tie antigens in the combination of related molecules, such as in the circumstance of purification of affinity.